第8章 使用 Express 快速进行 Web 开发
- 掌握使用 Express 处理静态资源
- 理解路由概念
- 掌握 Express 路由的基本使用
- 理解模板引擎概念
- 掌握模板引擎的基本使用
- 理解 Express 中间件执行模型
- 案例:Express 重写留言本案例
- 案例:基于文件的增删改查
- JSON 数据
原生的 http 模块在某些方面表现不足以应对我们的开发需求,所以我们就需要使用框架来加快我们的开发效率,框架的目的就是提高效率,让我们的代码更统一。
在 Node 中,有很多 Web 开发框架,我们这里以学习 为主。
- Express 是一个基于 Node.js 平台,快速、开放、极简的 web 开发框架。
- 作者:
- tj 个人博客
- 知名的开源项目创建者和协作者
- Express、commander、ejs、co、Koa…
- 已经离开 Node 社区,转 Go 了
- 丰富的 API 支持,强大而灵活的中间件特性
- Express 不对 Node.js 已有的特性进行二次抽象,只是在它之上扩展了 Web 应用所需的基本功能
- 有很多流行框架基于 Express
起步
Hello World
// 0. 加载 Expressconst express = require('express')// 1. 调用 express() 得到一个 app// 类似于 http.createServer()const app = express()// 2. 设置请求对应的处理函数// 当客户端以 GET 方法请求 / 的时候就会调用第二个参数:请求处理函数app.get('/', (req, res) => {res.send('hello world')})// 3. 监听端口号,启动 Web 服务app.listen(3000, () => console.log('app listening on port 3000!'))
基本路由
参考文档:
路由(Routing)是由一个 URI(或者叫路径标识)和一个特定的 HTTP 方法(GET、POST 等)组成的,涉及到应用如何处理响应客户端请求。
每一个路由都可以有一个或者多个处理器函数,当匹配到路由时,这个/些函数将被执行。
路由的定义的结构如下:
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER)
其中:
app是 express 实例METHOD是一个 HTTP 请求方法PATH是服务端路径(定位标识)HANDLER是当路由匹配到时需要执行的处理函数
下面是一些基本示例。
Respond with Hello World! on the homepage:
// 当你以 GET 方法请求 / 的时候,执行对应的处理函数app.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('Hello World!')})
Respond to POST request on the root route (/), the application’s home page:
// 当你以 POST 方法请求 / 的时候,指定对应的处理函数app.post('/', function (req, res) {res.send('Got a POST request')})
Respond to a PUT request to the /user route:
app.put('/user', function (req, res) {res.send('Got a PUT request at /user')})
Respond to a DELETE request to the /user route:
app.delete('/user', function (req, res) {res.send('Got a DELETE request at /user')})
For more details about routing, see the .
处理静态资源
// 开放 public 目录中的资源// 不需要访问前缀app.use(express.static('public'))// 开放 files 目录资源,同上app.use(express.static('files'))// 开放 public 目录,限制访问前缀app.use('/public', express.static('public'))// 开放 public 目录资源,限制访问前缀app.use('/static', express.static('public'))// 开放 publi 目录,限制访问前缀// path.join(__dirname, 'public') 会得到一个动态的绝对路径app.use('/static', express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')))
使用模板引擎
参考文档:
我们可以使用模板引擎处理服务端渲染,但是 Express 为了保持其极简灵活的特性并没有提供类似的功能。
同样的,Express 也是开放的,它支持开发人员根据自己的需求将模板引擎和 Express 结合实现服务端渲染的能力。
配置使用 art-template 模板引擎
参考文档:
这里我们以 模板引擎为例演示如何和 Express 结合使用。
安装:
npm install art-template express-art-template
配置:
// 第一个参数用来配置视图的后缀名,这里是 art ,则你存储在 views 目录中的模板文件必须是 xxx.art// app.engine('art', require('express-art-template'))// 这里我把 art 改为 htmlapp.engine('html', require('express-art-template'))
使用示例:
app.get('/', function (req, res) {// render 方法默认会去项目的 views 目录中查找 index.html 文件// render 方法的本质就是将读取文件和模板引擎渲染这件事儿给封装起来了res.render('index.html', {title: 'hello world'})})
如果希望修改默认的 views 视图渲染存储目录,可以:
// 第一个参数 views 是一个特定标识,不能乱写// 第二个参数给定一个目录路径作为默认的视图查找目录app.set('views', 目录路径)
其它常见模板引擎
JavaScript 模板引擎有很多,并且他们的功能都大抵相同,但是不同的模板引擎也各有自己的特色。
大部分 JavaScript 模板引擎都可以在 Node 中使用,下面是一些常见的模板引擎。
- ejs
- handlebars
- jade
- 后改名为 pug
- nunjucks
在 Express 中没有内置获取表单 POST 请求体的 API,这里我们需要使用一个第三方包:body-parser。
安装:
npm install --save body-parser
配置:
var express = require('express')// 0. 引包var bodyParser = require('body-parser')var app = express()// 配置 body-parser// 只要加入这个配置,则在 req 请求对象上会多出来一个属性:body// 也就是说你就可以直接通过 req.body 来获取表单 POST 请求体数据了// parse application/x-www-form-urlencodedapp.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }))// parse application/jsonapp.use(bodyParser.json())
使用:
app.use(function (req, res) {res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain')res.write('you posted:\n')// 可以通过 req.body 来获取表单 POST 请求体数据res.end(JSON.stringify(req.body, null, 2))})
使用 Session
安装:
npm install express-session
配置:
// 该插件会为 req 请求对象添加一个成员:req.session 默认是一个对象// 这是最简单的配置方式,暂且先不用关心里面参数的含义app.use(session({// 配置加密字符串,它会在原有加密基础之上和这个字符串拼起来去加密// 目的是为了增加安全性,防止客户端恶意伪造secret: 'itcast',resave: false,saveUninitialized: false // 无论你是否使用 Session ,我都默认直接给你分配一把钥匙}))
使用:
// 添加 Session 数据req.session.foo = 'bar'// 获取 Session 数据req.session.foo
提示:默认 Session 数据是内存存储的,服务器一旦重启就会丢失,真正的生产环境会把 Session 进行持久化存储。
路由
参考文档:
一个非常基础的路由:
var express = require('express')var app = express()// respond with "hello world" when a GET request is made to the homepageapp.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('hello world')})
路由方法
// GET method routeapp.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('GET request to the homepage')})// POST method routeapp.post('/', function (req, res) {res.send('POST request to the homepage')})
路由路径
This route path will match requests to the root route, /.
app.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('root')})
This route path will match requests to /about.
This route path will match requests to /random.text.
app.get('/random.text', function (req, res) {res.send('random.text')})
Here are some examples of route paths based on string patterns.
This route path will match acd and abcd.
app.get('/ab?cd', function (req, res) {res.send('ab?cd')})
This route path will match abcd, abbcd, abbbcd, and so on.
app.get('/ab+cd', function (req, res) {res.send('ab+cd')})
This route path will match abcd, abxcd, abRANDOMcd, ab123cd, and so on.
app.get('/ab*cd', function (req, res) {res.send('ab*cd')})
This route path will match /abe and /abcde.
app.get('/ab(cd)?e', function (req, res) {res.send('ab(cd)?e')})
Examples of route paths based on regular expressions:
This route path will match anything with an “a” in the route name.
res.send('/a/')})
This route path will match butterfly and dragonfly, but not butterflyman, dragonflyman, and so on.
app.get(/.*fly$/, function (req, res) {res.send('/.*fly$/')})
动态路径
Route path: /users/:userId/books/:bookIdRequest URL: http://localhost:3000/users/34/books/8989req.params: { "userId": "34", "bookId": "8989" }
定义动态的路由路径:
app.get('/users/:userId/books/:bookId', function (req, res) {res.send(req.params)})
路由处理方法
app.route()
express.Router
Create a router file named router.js in the app directory, with the following content:
const express = require('express')const router = express.Router()router.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('home page')})router.get('/about', function (req, res) {res.send('About page')})module.exports = router
Then, load the router module in the app:
const router = require('./router')// ...app.use(router)
在 Express 中获取客户端请求参数的三种方式
例如,有一个地址:/a/b/c?foo=bar&id=123
查询字符串参数
获取 ?foo=bar&id=123
console.log(req.query)
结果如下:
{foo: 'bar',id: '123'}
POST 请求才有请求体,我们需要单独配置 body-parser 中间件才可以获取。
只要程序中配置了 body-parser 中间件,我们就可以通过 来获取表单 POST 请求体数据。
req.body// => 得到一个请求体对象
动态的路径参数
在 Express 中,支持把一个路由设计为动态的。例如:
// /users/:id 要求必须以 /users/ 开头,:id 表示动态的,1、2、3、abc、dnsaj 任意都行// 注意::冒号很重要,如果你不加,则就变成了必须 === /users/id// 为啥叫 id ,因为是动态的路径,服务器需要单独获取它,所以得给它起一个名字// 那么我们就可以通过 req.params 来获取路径参数app.get('/users/:id', (req, res, next) => {console.log(req.params.id)})// /users/*/abc// req.params.idapp.get('/users/:id/abc', (req, res, next) => {console.log(req.params.id)})// /users/*/*// req.params.id// req.params.abcapp.get('/users/:id/:abc', (req, res, next) => {console.log(req.params.id)})// /*/*/*// req.params.usersapp.get('/:users/:id/:abc', (req, res, next) => {console.log(req.params.id)})// /*/id/*app.get('/:users/id/:abc', (req, res, next) => {console.log(req.params.id)})
参考文档:
Express 的最大特色,也是最重要的一个设计,就是中间件。一个 Express 应用,就是由许许多多的中间件来完成的。
为了理解中间件,我们先来看一下我们现实生活中的自来水厂的净水流程。
在上图中,自来水厂从获取水源到净化处理交给用户,中间经历了一系列的处理环节,我们称其中的每一个处理环节就是一个中间件。这样做的目的既提高了生产效率也保证了可维护性。
一个简单的中间件例子:打印日志
app.get('/', (req, res) => {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)res.send('index')})app.get('/about', (req, res) => {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)res.send('about')})app.get('/login', (req, res) => {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)res.send('login')})
在上面的示例中,每一个请求处理函数都做了一件同样的事情:请求日志功能(在控制台打印当前请求方法、请求路径以及请求时间)。
app.get('/', (req, res) => {// console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)logger(req)res.send('index')})app.get('/about', (req, res) => {// console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)logger(req)res.send('about')})app.get('/login', (req, res) => {// console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)logger(req)res.send('login')})function logger (req) {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)}
这样的做法自然没有问题,但是大家想一想,我现在只有三个路由,如果说有10个、100个、1000个呢?那我在每个请求路由函数中都手动调用一次也太麻烦了。
好了,我们不卖关子了,来看一下我们如何使用中间件来解决这个简单的小功能。
app.use((req, res, next) => {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)next()})app.get('/', (req, res) => {res.send('index')})app.get('/about', (req, res) => {res.send('about')})app.get('/login', (req, res) => {res.send('login')})function logger (req) {console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url} ${Date.now()}`)}
上面代码执行之后我们发现任何请求进来都会先在服务端打印请求日志,然后才会执行具体的业务处理函数。那这个到底是怎么回事?
中间件的组成
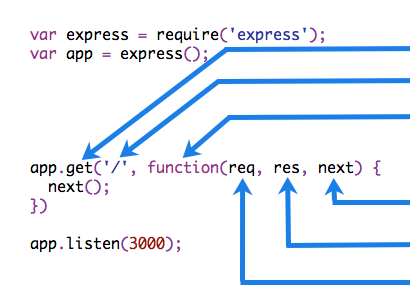
中间件函数可以执行以下任何任务:
- 执行任何代码
- 修改 request 或者 response 响应对象
- 结束请求响应周期
- 调用下一个中间件
中间件分类
- 应用程序级别中间件
- 路由级别中间件
- 错误处理中间件
- 内置中间件
- 第三方中间件
应用程序级别中间件
不关心请求路径:
var app = express()app.use(function (req, res, next) {console.log('Time:', Date.now())next()})
限定请求路径:
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {console.log('Request Type:', req.method)next()})
限定请求方法:
多个处理函数:
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)next()}, function (req, res, next) {console.log('Request Type:', req.method)next()})
多个路由处理函数:
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {console.log('ID:', req.params.id)next()}, function (req, res, next) {res.send('User Info')})// handler for the /user/:id path, which prints the user IDapp.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {res.end(req.params.id)})
最后一个例子:
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {// if the user ID is 0, skip to the next routeif (req.params.id === '0') next('route')// otherwise pass the control to the next middleware function in this stackelse next()}, function (req, res, next) {// render a regular pageres.render('regular')})// handler for the /user/:id path, which renders a special pageapp.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {res.render('special')})
路由级别中间件
创建路由实例:
var router = express.Router()
示例:
var app = express()var router = express.Router()// a middleware function with no mount path. This code is executed for every request to the routerrouter.use(function (req, res, next) {console.log('Time:', Date.now())next()})// a middleware sub-stack shows request info for any type of HTTP request to the /user/:id pathrouter.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)next()}, function (req, res, next) {console.log('Request Type:', req.method)next()})// a middleware sub-stack that handles GET requests to the /user/:id pathrouter.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {// if the user ID is 0, skip to the next routerif (req.params.id === '0') next('route')// otherwise pass control to the next middleware function in this stackelse next()}, function (req, res, next) {// render a regular pageres.render('regular')})// handler for the /user/:id path, which renders a special pagerouter.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {console.log(req.params.id)res.render('special')})// mount the router on the appapp.use('/', router)
另一个示例:
var app = express()var router = express.Router()// predicate the router with a check and bail out when neededrouter.use(function (req, res, next) {if (!req.headers['x-auth']) return next('router')})router.get('/', function (req, res) {res.send('hello, user!')})// use the router and 401 anything falling throughapp.use('/admin', router, function (req, res) {res.sendStatus(401)})
错误处理中间件
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {console.error(err.stack)res.status(500).send('Something broke!')})
内置中间件
- serves static assets such as HTML files, images, and so on.
- express.json parses incoming requests with JSON payloads. NOTE: Available with Express 4.16.0+
- parses incoming requests with URL-encoded payloads. NOTE: Available with Express 4.16.0+
官方支持的中间件列表:
第三方中间件
官方中间件资源:
早期的 Express 内置了很多中间件。后来 Express 在 4.x 之后移除了这些内置中间件,官方把这些功能性中间件以包的形式单独提供出来。这样做的目的是为了保持 Express 本身极简灵活的特性,开发人员可以根据自己的需求去灵活的定制。下面是官方提供的一些常用的中间件解决方案。
中间件应用
输出请求日志中间件
功能:实现为任何请求打印请求日志的功能。
logger.js 定义并导出一个中间件处理函数:
module.exports = (req, res, next) => {console.log(`${req.method} -- ${req.path}`)next()}
app.js 加载使用中间件处理函数:
app.use(logger)
统一处理静态资源中间件
static.js 定义并导出一个中间件处理函数:
const fs = require('fs')const path = require('path')module.exports = function static(pathPrefix) {return function (req, res, next) {const filePath = path.join(pathPrefix, req.path)fs.readFile(filePath, (err, data) => {if (err) {// 继续往后匹配查找能处理该请求的中间件// 如果找不到,则 express 会默认发送 can not get xxxreturn next()}res.end(data)})}}
app.js 加载并使用 static 中间件处理函数:
// 不限定请求路径前缀app.use(static('./public'))app.use(static('./node_modules'))// 限定请求路径前缀app.use('/public', static('./public'))app.use('/node_modules', static('./node_modules'))
错误处理
参考文档:
常用 API
参考文档:
express
- express.json
- express.static
- express.Router
- express.urlencoded()
Application
- app.set
- app.get
- app.locals
Request
- req.app
- req.query
- req.body
- req.cookies
- req.ip
- req.hostname
- Req.method
- req.params
- req.path
- req.get()
Response
- res.locals
- res.append()
- res.cookie()
- res.clearCookie()
- res.download()
- res.end()
- res.json()
- res.jsonp()
- res.redirect()
- res.render()
- res.send()
- res.sendStatus()
- res.set()
- res.status()
Router
- router.all()
- router.METHOD()
- router.use()
小案例
案例Github仓库地址:https://github.com/lipengzhou/express-guestbook-case
完整目录结构如下:
.├── node_modules npm安装的第三方包目录,使用 npm 装包会自动创建├── public 页面需要使用的静态资源│ ├── css│ ├── js│ ├── img│ └── ...├── views 所有视图页面(只存储 html 文件)│ ├── publish.html│ └── index.html├── app.js 服务端程序入口文件,执行该文件会启动我们的 Web 服务器├── db.json 这里充当我们的数据库├── README.md 项目说明文档├── package.json 项目包说明文件,存储第三方包依赖等信息└── package-lock.json npm的包锁定文件,用来锁定第三方包的版本和提高npm下载速度
# 创建项目目录mkdir guestbook# 进入项目目录cd guestbook# 初始化 package.json 文件npm init -y# 将 Express 安装到项目中npm install express
一、Hello World
// 0. 加载 Expressconst express = require('express')// 1. 调用 express() 得到一个 app// 类似于 http.createServer()const app = express()// 2. 设置请求对应的处理函数// 当客户端以 GET 方法请求 / 的时候就会调用第二个参数:请求处理函数app.get('/', (req, res) => {res.send('hello world')})// 3. 监听端口号,启动 Web 服务app.listen(3000, () => console.log('app listening on port 3000!'))
二、配置模板引擎
参见:Express - 使用模板引擎
三、路由设计
| 请求方法 | 请求路径 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| GET | / | 渲染 index.html |
| GET | /publish | 渲染 publish.html |
| POST | /publish | 处理发表留言 |
app.get('/', function (req, res) {// ...})app.get('/publish', function (req, res) {// ...})app.post('/publish', function (req, res) {// ...})
四、走通页面渲染跳转
app.get('/', function (req, res) {res.render('index.html')})app.get('/publish', function (req, res) {res.render('publish.html')})
五、安装处理 Bootstrap 样式文件
安装 bootstrap 到项目中:
npm install bootstrap
将 node_modules 目录开放出来:
app.use('/node_modules/', express.static('./node_modules/'))
六、将数据库中的 post 渲染到首页
JavaScript 后台处理:
app.get('/', function (req, res) {fs.readFile('./db.json', function (err, data) {if (err) {return res.render('500.html', {errMessage: err.message})}try {data = JSON.parse(data.toString())res.render('index.html', {posts: data.posts})} catch (err) {return res.render('500.html', {errMessage: err.message})}})})
<ul class="list-group">{{ each posts }}<li class="list-group-item"><span class="badge">{{ $value.time }}</span><span>{{ $value.name }}</span>说:<span>{{ $value.content }}</span></li>{{ /each }}</ul>
七、配置解析表单 post 请求体
参见:Express - 解析表单 post 请求体
八、处理 publish 表单提交
九、案例优化:提取数据操作模块
const {readFile, writeFile} = require('fs')const dbPath = './db.json'exports.getDb = getDb// 封装带来的好处:// 1. 可维护性// 2. 其次才是重用exports.addPost = (post, callback) => {getDb((err, dbData) => {if (err) {return callback(err)}// 获取数组中最后一个元素const last = dbData.posts[dbData.posts.length - 1]// 添加数据的 id 自动增长post.id = last ? last.id + 1 : 1// 创建时间post.createdAt = '2018-2-2 11:57:06'// 将数据添加到数组中(这里还并没有持久化存储)dbData.posts.push(post)// 将 dbData 对象转成字符串持久化存储到文件中const dbDataStr = JSON.stringify(dbData)writeFile(dbPath, dbDataStr, err => {if (err) {return callback(err)}// Express 为 res 响应对象提供了一个工具方法:redirect 可以便捷的重定向// res.redirect('/')callback(null)})})}function getDb (callback) {readFile(dbPath, 'utf8', (err, data) => {if (err) {return callback(err)}callback(null, JSON.parse(data))})


